Jim Nabors: Actor, Singer, and Comedian
On November 30, 2017, Jim Nabors, perhaps most famous for his role as Gomer Pyle, died at the age of 87. Jim is survived by his husband Stan Cadwallader, whom he married in 2013. Their marriage came one month after same-sex marriages became legal in Washington State.
It is quite eye-opening to look at the tax consequences of their decision to get married; Mr. Nabors died with a $13M estate. The terms of his will are not public, but for the sake of argument let’s assume he left his estate to his husband. Because of the marriage, no Federal or Hawaiian estate or inheritance taxes are due at death because of the unlimited marital deduction.
Smart Estate Planning
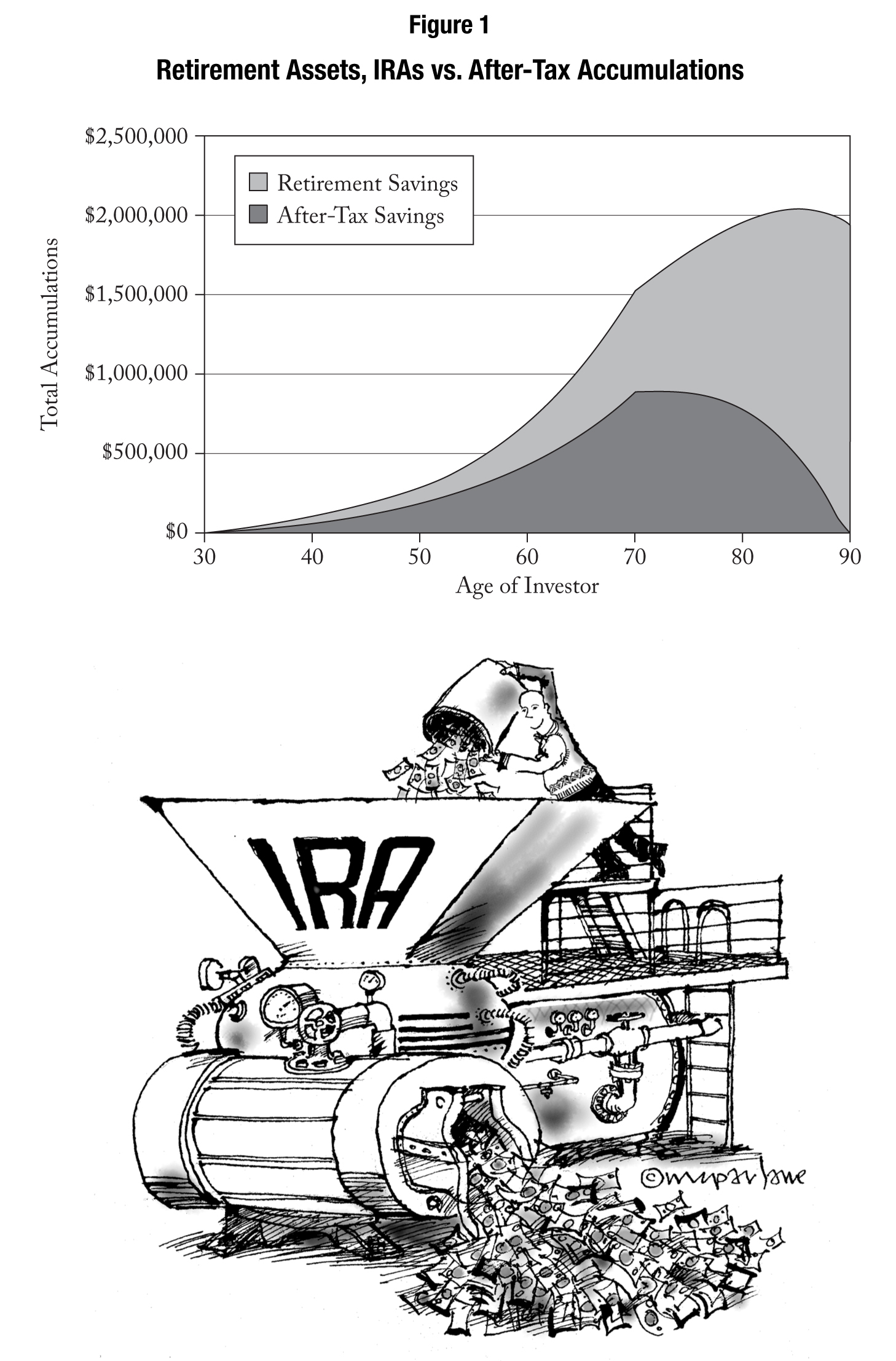
If Jim and Stan had remained unmarried partners the payout to the Government would have been astronomical. A $3,000,000 payment in federal estate taxes alone is bad enough. A payment of over $1,800,000 in Hawaiian inheritance taxes would add a total of $4,800,000 in total taxes. These numbers don’t include the income taxes that will be saved because of the longer “stretch” a spouse receives on an inherited IRA or retirement plan.
The moral of the story is that for many life-long partners, gay or straight: Get Married for the Money. Obviously the decision to marry hinges on more than whether marriage is a financially strategic move. But if you are simply avoiding the formalities, it might make sense to think about the long-term tax consequences on your financial security—for both you and your partner. Marriage is usually a big plus for purposes of Social Security, especially if one partner has a much stronger earnings record than the other partner.
More Information Is Always Available
For more information visit www.paytaxeslater.com.To schedule an appointment with Jim Lange, please call his office at 412-521-2732. You can always contact Jim at jim@paytaxeslater.com.
James Lange, CPA/Attorney of Lange Financial Group, LLC, is the author of several books on retirement and estate planning, including Live Gay, Retire Rich. His books on retirement strategies have been endorsed by Charles Schwab, Larry King, Jane Bryant Quinn, Ed Slott, and many more. He hosts a weekly financial show on KQV News Radio in Pittsburgh. PA.



 A nationally recognized IRA, Roth IRA conversion, and 401(k) expert, he is a regular speaker to both consumers and professional organizations. Jim is the creator of the Lange Cascading Beneficiary Plan™, a benchmark in retirement planning with the flexibility and control it offers the surviving spouse, and the founder of The Roth IRA Institute, created to train and educate financial advisors.
A nationally recognized IRA, Roth IRA conversion, and 401(k) expert, he is a regular speaker to both consumers and professional organizations. Jim is the creator of the Lange Cascading Beneficiary Plan™, a benchmark in retirement planning with the flexibility and control it offers the surviving spouse, and the founder of The Roth IRA Institute, created to train and educate financial advisors.